![]() Netdata is an open source tool designed to collect real-time metrics, such as CPU usage, disk activity, bandwidth usage, website visits, etc., and then display them in live, easy-to-interpret charts. This post will cover how to create a Netdata “parent’ for centralized collecting of all the children. In a later post this will be integrated with Prometheus and Grafana to provide centralized reporting.
Netdata is an open source tool designed to collect real-time metrics, such as CPU usage, disk activity, bandwidth usage, website visits, etc., and then display them in live, easy-to-interpret charts. This post will cover how to create a Netdata “parent’ for centralized collecting of all the children. In a later post this will be integrated with Prometheus and Grafana to provide centralized reporting.
This blog entry will only cover the Netdata collection of the following picture. Multiple Netdata child nodes will gather information of their Host and forward this information to the Netdata parent node. Another blog entry will cover the Time-Series database and Grafana configuration.
Step 1: Parent Server
Install the Netdata software package
# apt install netdata
Generate a random uuid number with uuidgen command so we can use it as a generic API-KEY
# uuidgen 889a1dd0-7842-4034-92dc-10c90fb34b93
Generate a stream configuration file by using the following command, if you like to use this editor you can stay in it, else ctrl-x, save
# cd /etc/netdata # ./edit-config stream.conf
Edit the configuration file /etc/netdata/stream.conf and in the API-KEY section change it
[889a1dd0-7842-4034-92dc-10c90fb34b93] # Default settings for this API key # You can disable the API key, by setting this to: no # The default (for unknown API keys) is: no enabled = yes # A list of simple patterns matching the IPs of the servers that # will be pushing metrics using this API key. # The metrics are received via the API port, so the same IPs # should also be matched at netdata.conf [web].allow connections from allow from = 192.168.* # The default history in entries, for all hosts using this API key. # You can also set it per host below. # If you don't set it here, the history size of the central netdata # will be used. default history = 3600 # The default memory mode to be used for all hosts using this API key. # You can also set it per host below. # If you don't set it here, the memory mode of netdata.conf will be used. # Valid modes: # save save on exit, load on start # map like swap (continuously syncing to disks - you need SSD) # ram keep it in RAM, don't touch the disk # none no database at all (use this on headless proxies) # dbengine like a traditional database default memory mode = ram # Shall we enable health monitoring for the hosts using this API key? # 3 possible values: # yes enable alarms # no do not enable alarms # auto enable alarms, only when the sending netdata is connected. For ephemeral child nodes or child system restarts, # ensure that the netdata process on the child is gracefully stopped, to prevent invalid last_collected alarms # You can also set it per host, below. # The default is taken from [health].enabled of netdata.conf health enabled by default = auto # postpone alarms for a short period after the sender is connected default postpone alarms on connect seconds = 60
In our case we like to keep all data-in-transit communications encrypted, so we generated a specific SSL key and certificate for our services and placed these in the Netdata directory as so:
# ls -l /etc/netdata/ssl/ total 8 -rw-r--r-- 1 netdata netdata 3750 Dec 12 02:56 netdata.crt -rw------- 1 netdata netdata 1679 Dec 12 02:55 netdata.key
Change the Netdata configuration file so that it accepts data on the network port and only accepts encrypted communications by editing /etc/netdata/netdata.conf
[global]
run as user = netdata
web files owner = root
web files group = root
bind to = *=dashboard|registry|badges|management|streaming|netdata.conf^SSL=optional
[web]
ssl key = /etc/netdata/ssl/netdata.key
ssl certificate = /etc/netdata/ssl/netdata.crt
Restart the services and make sure it remains enabled
# systemctl restart netdata # systemctl enable netdata
Tryout Netdata by going to the url https://<netdata_parent>:19999
Step 2: Child Server
Install the Netdata software package on your “children” to forward their data to the “parent”
# apt install netdata
Generate a stream configuration file by using the following command, if you like to use this editor you can stay in it, else ctrl-x, save
# cd /etc/netdata # ./edit-config stream.conf
Edit the configuration file /etc/netdata/stream.conf define the destination IP of the parent (SSL enabled), and the API key. There are two methods to verify the parent SSL certificate: skip-check or define a location of the CA certificate, in my case I define a CA certificate location
[stream]
# Enable this on child nodes, to have them send metrics.
enabled = yes
# Where is the receiving netdata?
# A space separated list of:
#
# [PROTOCOL:]HOST[%INTERFACE][:PORT][:SSL]
#
# If many are given, the first available will get the metrics.
#
# PROTOCOL = tcp, udp, or unix (only tcp and unix are supported by parent nodes)
# HOST = an IPv4, IPv6 IP, or a hostname, or a unix domain socket path.
# IPv6 IPs should be given with brackets [ip:address]
# INTERFACE = the network interface to use (only for IPv6)
# PORT = the port number or service name (/etc/services)
# SSL = when this word appear at the end of the destination string
# the Netdata will encrypt the connection with the parent.
#
# This communication is not HTTP (it cannot be proxied by web proxies).
destination = 192.168.22.233:19999:SSL
# Skip Certificate verification?
#
# The netdata child is configurated to avoid invalid SSL/TLS certificate,
# so certificates that are self-signed or expired will stop the streaming.
# Case the server certificate is not valid, you can enable the use of
# 'bad' certificates setting the next option as 'yes'.
#
# ssl skip certificate verification = yes
# Certificate Authority Path
#
# OpenSSL has a default directory where the known certificates are stored,
# case it is necessary it is possible to change this rule using the variable
# "CApath"
#
#CApath = /etc/ssl/certs/
# Certificate Authority file
#
# When the Netdata parent has certificate, that is not recognized as valid,
# we can add this certificate in the list of known certificates in CApath
# and give for Netdata as argument.
#
CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/CA-file.pem
# The API_KEY to use (as the sender)
api key = 889a1dd0-7842-4034-92dc-10c90fb34b93
# The timeout to connect and send metrics
timeout seconds = 60
# If the destination line above does not specify a port, use this
# default port = 19999
# filter the charts to be streamed
# netdata SIMPLE PATTERN:
# - space separated list of patterns (use \ to include spaces in patterns)
# - use * as wildcard, any number of times within each pattern
# - prefix a pattern with ! for a negative match (ie not stream the charts it matches)
# - the order of patterns is important (left to right)
# To send all except a few, use: !this !that * (ie append a wildcard pattern)
send charts matching = *
# The buffer to use for sending metrics.
Change the Netdata configuration file so that it it does not store local information, not open up the API port and only forward information by editing /etc/netdata/netdata.conf
[global]
run as user = netdata
web files owner = root
web files group = root
# disable the local database
memory mode = none
[web]
# Disables the API (Netdata will not listen to any ports).
# This also disables the registry (there cannot be a registry without an API).
mode = none
Restart the services and make sure it remains enabled
# systemctl restart netdata # systemctl enable netdata
Step 3: View Data
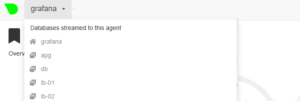
Tryout Netdata by going to the url https://<netdata_parent>:19999 once data is received by the parent a drop down box should become available in the top left hand corner where you can select each child host and view its data.
For any errors monitor your Netdata log file /var/log/netdata/netdata.log for any errors or information when pushing data from the child or receiving from the parent. Also collection of specific data from Netdata (Squid, Apache, Bind) requires specific configuration, review the Netdata documentation for information.
Step 4: Disable Cloud
During runtime netdata can create a large amount of log file messages as defined below:
Netdata : CONFIG: cannot load cloud config ‘/var/lib/netdata/cloud.d/cloud.conf’. Running with internal defaults
To disable this create a file under /var/lib/netdata/cloud.d/cloud.conf with the following data
[global] enabled = no
Change the properties of the file to the following:
# chmod 0770/var/lib/netdata/cloud.d/cloud.conf# chown netdata:netdata/var/lib/netdata/cloud.d/cloud.conf
Step 5: Disable Health
If you monitor health at other levels, you can specifically disable health monitoring on the children by editing /etc/netdata/netdata.conf and adding a [health] section
[health] enabled = no